Triple Integrals
Introduction
Triple integrals are more difficult (in fact, usually impossible) to picture than double integrals, but the principle is much the same. Instead of integrals like
∬ R f ( x , y ) d A , \iint_R f(x,y) \ dA, ∬ R f ( x , y ) d A , ∭ D f ( x , y , z ) d V \iiint_D f(x,y,z)\ dV ∭ D f ( x , y , z ) d V D D D 3 3 3
Note
The volume of D D D Volume = ∭ D d z d y d x \textrm{Volume } = \iiint_D\ dz\ dy\ dx Volume = ∭ D d z d y d x
Again, the challenge with triple integrals really lies with finding the limits of integration; once we have those, we simply have to carry out the integration, which usually isn't too complicated.
Evaluate the following triple integral.
∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 ∫ 0 2 d x d y d x \int_0^2 \int_0^3 \int_0^2\ dx\ dy\ dx ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 ∫ 0 2 d x d y d x
Solution
∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 ∫ 0 2 d x d y d x = ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 2 d y d x = ∫ 0 2 6 d x = 12 \begin{aligned}
\int_0^2 \int_0^3 \int_0^2\ dx\ dy\ dx &= \int_0^2 \int_0^3 2\ dy\ dx\
&= \int_0^2 6\ dx = \ans{12}
\end{aligned} ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 ∫ 0 2 d x d y d x = ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 2 d y d x = ∫ 0 2 6 d x = 1 2
Note that this gives the volume of a 2 × 3 × 2 2×3×2 2 × 3 × 2
Use a triple integral to find the volume of the prism D D D y = 4 − 2 x y=4−2x y = 4 − 2 x z = 6 z=6 z = 6
Solution
Note that this prism is
D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 4 − 2 x , 0 ≤ z ≤ 6 } D={(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq 2,\ 0 \leq y \leq 4-2x,\ 0 \leq z \leq 6} D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 4 − 2 x , 0 ≤ z ≤ 6 } D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 − 1 2 y , 0 ≤ y ≤ 4 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 6 } D={(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq 2-\dfrac{1}{2}y,\ 0 \leq y \leq 4,\ 0 \leq z \leq 6} D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 − 2 1 y , 0 ≤ y ≤ 4 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 6 }
We can write this integral in several ways, all of which give the same answer:
V = ∫ 0 6 ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − 2 x d y d x d z = ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − 2 x ∫ 0 6 d x d y d x = ∫ 0 6 ∫ 0 4 ∫ 0 2 − y / 2 d x d y d z = 24 \begin{aligned}
V &= \int_0^6 \int_0^2 \int_0^{4-2x} \ dy\ dx\ dz\
&= \int_0^2 \int_0^{4-2x} \int_0^6 \ dx\ dy\ dx\
&= \int_0^6 \int_0^4 \int_0^{2-y/2} \ dx\ dy\ dz\
&= \ans{24}
\end{aligned} V = ∫ 0 6 ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − 2 x d y d x d z = ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − 2 x ∫ 0 6 d x d y d x = ∫ 0 6 ∫ 0 4 ∫ 0 2 − y / 2 d x d y d z = 2 4
Notice that in each case, we have to make sure that we use the limits that involve one variable before we integrate with respect to that variable.
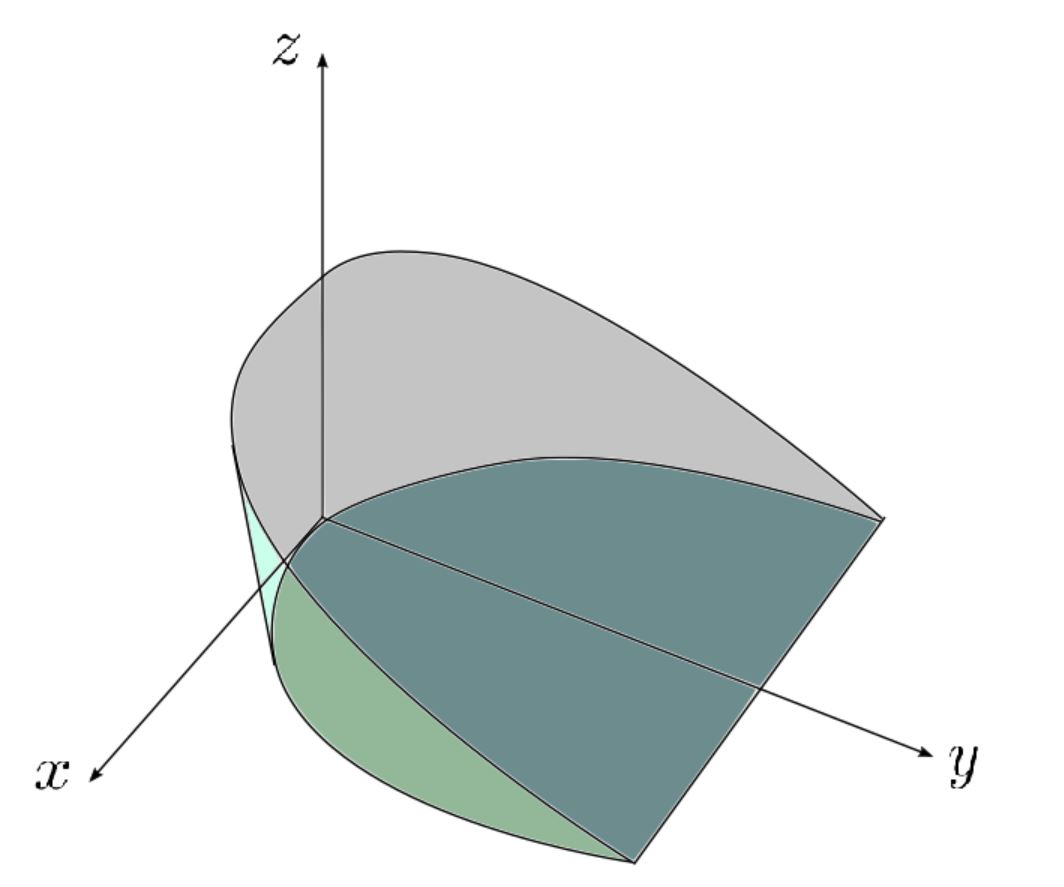
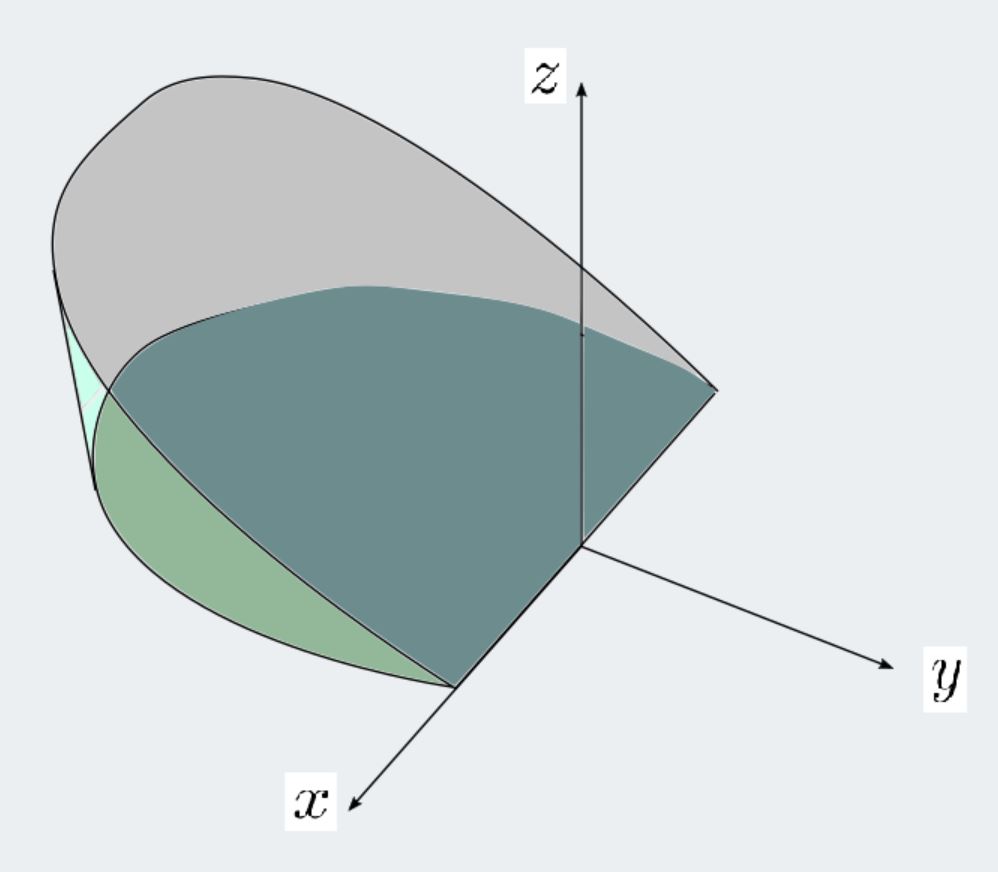
Find the volume of the solid in the first octant bounded by the plane 2 x + 3 y + 6 z = 12 2x+3y+6z=12 2 x + 3 y + 6 z = 1 2
∫ 0 4 ∫ 0 6 − 3 y / 2 ∫ 0 12 − 2 x − 3 y d z d x d y = ∫ 0 6 ∫ 0 4 − 2 x / 3 ∫ 0 12 − 2 x − 3 y d z d y d x = 8 \displaystyle\int_0^4 \displaystyle\int_0^{6-3y/2} \displaystyle\int_0^{12-2x-3y} \ dz\ dx\ dy = \displaystyle\int_0^6 \displaystyle\int_0^{4-2x/3} \displaystyle\int_0^{12-2x-3y} \ dz\ dy\ dx = 8 ∫ 0 4 ∫ 0 6 − 3 y / 2 ∫ 0 1 2 − 2 x − 3 y d z d x d y = ∫ 0 6 ∫ 0 4 − 2 x / 3 ∫ 0 1 2 − 2 x − 3 y d z d y d x = 8
Simple Applications
Mass
If the density of a body is a function of position (ρ = f ( x , y , z ) ρ=f(x,y,z) ρ = f ( x , y , z ) M = ∭ D f ( x , y , z ) d V M = \iiint_D f(x,y,z)\ dV M = ∭ D f ( x , y , z ) d V
If the density function is given by ρ = 2 − z ρ=2−z ρ = 2 − z 3 ^3 3 D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 3 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 1 } , D={(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq 3,\ 0 \leq y \leq 2,\ 0 \leq z \leq 1}, D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 3 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 1 } ,
Solution
M = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 2 − z d x d y d z = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 6 − 3 z d y d z = ∫ 0 1 12 − 6 z d z = 12 z − 3 z 2 ∣ 0 1 = 9 k g \begin{aligned}
M &= \int_0^1 \int_0^2 \int_0^3 2-z\ dx\ dy\ dz\
&= \int_0^1 \int_0^2 6-3z\ dy\ dz\
&= \int_0^1 12-6z\ dz\
&= 12z-3z^2 \bigg|_0^1 = \ans{9\ kg}
\end{aligned} M = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 3 2 − z d x d y d z = ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 6 − 3 z d y d z = ∫ 0 1 1 2 − 6 z d z = 1 2 z − 3 z 2 ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 0 1 = 9 k g
Average Value
The average value of f ( x , y , z ) f(x,y,z) f ( x , y , z ) f ‾ = 1 volume of D ∭ D f ( x , y , z ) d V \overline{f} = \dfrac{1}{\textrm{volume of } D} \iiint_D f(x,y,z)\ dV f = volume of D 1 ∭ D f ( x , y , z ) d V
Find the average value of f ( x , y , z ) = 250 x y sin ( π z ) f(x,y,z)=250xy \sin(πz) f ( x , y , z ) = 2 5 0 x y sin ( π z ) D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 1 } . D={(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq 2,\ 0 \leq y \leq 2,\ 0 \leq z \leq 1}. D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 1 } .
Solution
f ‾ = 1 4 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 2 250 x y sin ( π z ) d x d y d z = 1 4 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 500 y sin ( π z ) d y d z = 1 4 ∫ 0 1 1000 sin ( π z ) d z = 1 4 [ − 1000 ⋅ 1 π cos ( π z ) ] 0 1 = 500 π \begin{aligned}
\overline{f} &= \dfrac{1}{4} \int_0^1 \int_0^2 \int_0^2 250 xy \sin (\pi z) \ dx\ dy\ dz\
&= \dfrac{1}{4} \int_0^1 \int_0^2 500 y \sin (\pi z) \ dy\ dz\
&= \dfrac{1}{4} \int_0^1 1000 \sin (\pi z)\ dz\
&= \dfrac{1}{4} \bigg[ -1000 \cdot \dfrac{1}{\pi} \cos (\pi z) \bigg]_0^1\
&= \ans{\dfrac{500}{\pi}}
\end{aligned} f = 4 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 2 2 5 0 x y sin ( π z ) d x d y d z = 4 1 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 2 5 0 0 y sin ( π z ) d y d z = 4 1 ∫ 0 1 1 0 0 0 sin ( π z ) d z = 4 1 [ − 1 0 0 0 ⋅ π 1 cos ( π z ) ] 0 1 = π 5 0 0
Find the average value of f ( x , y , z ) = 128 e − x − y − z f(x,y,z) = 128e^{-x-y-z} f ( x , y , z ) = 1 2 8 e − x − y − z D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ ln 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ ln 4 , 0 ≤ z ≤ ln 8 } D = {(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq \ln 2, 0 \leq y \leq \ln 4, 0 \leq z \leq \ln 8} D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ ln 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ ln 4 , 0 ≤ z ≤ ln 8 }
1 ( ln 2 ) ( ln 4 ) ( ln 8 ) ∫ 0 ln 8 ∫ 0 ln 4 ∫ 0 ln 2 128 e − x − y − z d x d y d z = 7 ( ln 2 ) 3 \dfrac{1}{(\ln 2)(\ln 4)(\ln 8)}\displaystyle\int_0^{\ln 8} \displaystyle\int_0^{\ln 4} \displaystyle\int_0^{\ln 2} 128e^{-x-y-z}\ dx\ dy\ dz = \dfrac{7}{(\ln 2)^3} ( ln 2 ) ( ln 4 ) ( ln 8 ) 1 ∫ 0 ln 8 ∫ 0 ln 4 ∫ 0 ln 2 1 2 8 e − x − y − z d x d y d z = ( ln 2 ) 3 7
Examples
Evaluate ∭ D 2 x d V \displaystyle\iiint_D 2x\ dV ∭ D 2 x d V D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ x ≤ 4 − y 2 , 0 ≤ z ≤ y } . D={(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq y \leq 2,\ 0 \leq x \leq \sqrt{4-y^2},\ 0 \leq z \leq y}. D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 , 0 ≤ x ≤ 4 − y 2 , 0 ≤ z ≤ y } .
Solution
∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − y 2 ∫ 0 y 2 x d z d x d y = ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − y 2 2 x y d x d y = ∫ 0 2 ( 4 − y 2 ) y d y = 2 y − 1 4 y 4 ∣ 0 2 = 4 \begin{aligned}
\int_0^2 \int_0^{\sqrt{4-y^2}} \int_0^y &2x\ dz\ dx\ dy\
&= \int_0^2 \int_0^{\sqrt{4-y^2}} 2xy \ dx\ dy\
&= \int_0^2 (4-y^2)y\ dy\
&= 2y-\dfrac{1}{4}y^4 \bigg|_0^2 = \ans{4}
\end{aligned} ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − y 2 ∫ 0 y 2 x d z d x d y = ∫ 0 2 ∫ 0 4 − y 2 2 x y d x d y = ∫ 0 2 ( 4 − y 2 ) y d y = 2 y − 4 1 y 4 ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 0 2 = 4
Find the volume of the solid in the first octant formed when the cylinder z = sin y z=\sin y z = sin y 0 ≤ y ≤ π 0≤y≤π 0 ≤ y ≤ π y = x y=x y = x x = 0 x=0 x = 0
Solution
Note that D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ y , 0 ≤ y ≤ π , 0 ≤ z ≤ sin y } . D={(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq y,\ 0 \leq y \leq \pi,\ 0 \leq z \leq \sin y}. D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ y , 0 ≤ y ≤ π , 0 ≤ z ≤ sin y } .
The volume, then, is given by
V = ∫ 0 π ∫ 0 y ∫ 0 sin y d z d x d y = ∫ 0 π ∫ 0 y sin y d x d y = ∫ 0 π y sin y d y = − y cos y + sin y ∣ 0 π (using Integration by Parts) = π \begin{aligned}
V &= \int_0^\pi \int_0^y \int_0^{\sin y} \ dz\ dx\ dy\
&= \int_0^\pi \int_0^y \sin y\ dx\ dy\
&= \int_0^\pi y \sin y\ dy\
&= -y\cos y + \sin y \bigg|_0^\pi \ \ \ \textrm{ (using Integration by Parts)}\
&= \ans{\pi}
\end{aligned} V = ∫ 0 π ∫ 0 y ∫ 0 sin y d z d x d y = ∫ 0 π ∫ 0 y sin y d x d y = ∫ 0 π y sin y d y = − y cos y + sin y ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 0 π (using Integration by Parts) = π
Find the volume of the prism in the first octant bounded by z = 2 − 4 x z=2−4x z = 2 − 4 x y = 8 y=8 y = 8
Solution
Note that
D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 / 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 8 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 2 − 4 x } . D={(x,y,z)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq 1/2,\ 0 \leq y \leq 8,\ 0 \leq z \leq 2-4x}. D = { ( x , y , z ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 / 2 , 0 ≤ y ≤ 8 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 2 − 4 x } .
The volume, then, is given by
V = ∫ 0 8 ∫ 0 1 / 2 ∫ 0 2 − 4 x d z d x d y = ∫ 0 8 ∫ 0 1 / 2 2 − 4 x d x d y = ∫ 0 8 [ 2 x − 2 x 2 ] 0 1 / 2 d y = ∫ 0 8 1 2 d y = 4 \begin{aligned}
V &= \int_0^8 \int_0^{1/2} \int_0^{2-4x} \ dz\ dx\ dy\
&= \int_0^8 \int_0^{1/2} 2-4x\ dx\ dy\
&= \int_0^8 \bigg[ 2x-2x^2 \bigg]_0^{1/2}\ dy\
&= \int_0^8 \dfrac{1}{2}\ dy = \ans{4}
\end{aligned} V = ∫ 0 8 ∫ 0 1 / 2 ∫ 0 2 − 4 x d z d x d y = ∫ 0 8 ∫ 0 1 / 2 2 − 4 x d x d y = ∫ 0 8 [ 2 x − 2 x 2 ] 0 1 / 2 d y = ∫ 0 8 2 1 d y = 4
Find the volume of the wedge bounded by the parabolic cylinder y = x 2 y=x^2 y = x 2 z = 3 − y z=3−y z = 3 − y z = 0 z=0 z = 0
Solution
Note that
D = { ( x , y , z ) : − 3 ≤ x ≤ 3 , x 2 ≤ y ≤ 3 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 3 − y } . D={(x,y,z)\ :\ -\sqrt{3} \leq x \leq \sqrt{3},\ x^2 \leq y \leq 3,\ 0 \leq z \leq 3-y}. D = { ( x , y , z ) : − 3 ≤ x ≤ 3 , x 2 ≤ y ≤ 3 , 0 ≤ z ≤ 3 − y } .
The volume, then, is given by
V = ∫ − 3 3 ∫ x 2 3 ∫ 0 3 − y d z d y d x = ∫ − 3 3 ∫ x 2 3 3 − y d y d x = ∫ − 3 3 9 2 − 3 x 2 + 1 2 x 4 d x = 9 2 x − x 3 + 1 10 x 5 ∣ − 3 3 = 24 3 5 \begin{aligned}
V &= \int_{-\sqrt{3}}^{\sqrt{3}} \int_{x^2}^{3} \int_0^{3-y} \ dz\ dy\ dx\
&= \int_{-\sqrt{3}}^{\sqrt{3}} \int_{x^2}^{3} 3-y\ dy\ dx\
&= \int_{-\sqrt{3}}^{\sqrt{3}} \dfrac{9}{2}-3x^2+\dfrac{1}{2}x^4\ dx\
&= \dfrac{9}{2}x-x^3+\dfrac{1}{10}x^5 \bigg|_{-\sqrt{3}}^{\sqrt{3}} = \ans{\dfrac{24\sqrt{3}}{5}}
\end{aligned} V = ∫ − 3 3 ∫ x 2 3 ∫ 0 3 − y d z d y d x = ∫ − 3 3 ∫ x 2 3 3 − y d y d x = ∫ − 3 3 2 9 − 3 x 2 + 2 1 x 4 d x = 2 9 x − x 3 + 1 0 1 x 5 ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ − 3 3 = 5 2 4 3
Evaluate the integral ∭ D x y + x z + y z d V \displaystyle\iiint_D xy+xz+yz\ dV ∭ D x y + x z + y z d V D = { ( x , y , z ) : − 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 , − 2 ≤ y ≤ 2 , − 1 ≤ z ≤ 3 } D = {(x,y,z)\ :\ -1 \leq x \leq 1, -2 \leq y \leq 2, -1 \leq z \leq 3} D = { ( x , y , z ) : − 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 , − 2 ≤ y ≤ 2 , − 1 ≤ z ≤ 3 }
0 0 0
Find the volume of the wedge above the x y xy x y x 2 + y 2 = 4 x^2+y^2=4 x 2 + y 2 = 4 z = 0 z=0 z = 0 z = − y z=−y z = − y
∫ − 2 2 ∫ − 4 − x 2 0 ∫ 0 − y d z d y d x = 16 3 \displaystyle\int_{-2}^2 \displaystyle\int_{-\sqrt{4-x^2}}^0 \displaystyle\int_0^{-y} \ dz\ dy\ dx = \dfrac{16}{3} ∫ − 2 2 ∫ − 4 − x 2 0 ∫ 0 − y d z d y d x = 3 1 6
Find the volume of the solid bounded by the surfaces z = e y z=e^y z = e y z = 1 z=1 z = 1 { ( x , y ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 , 0 ≤ y ≤ ln 2 } . {(x,y)\ :\ 0 \leq x \leq 1, 0 \leq y \leq \ln 2}. { ( x , y ) : 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 , 0 ≤ y ≤ ln 2 } .
∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 ln 2 ∫ 1 e y d z d y d x = 1 − ln 2 \displaystyle\int_0^1 \displaystyle\int_0^{\ln 2} \displaystyle\int_1^{e^y} \ dz\ dy\ dx = 1-\ln 2 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 ln 2 ∫ 1 e y d z d y d x = 1 − ln 2
Find the volume of the wedge of the cylinder x 2 + 4 y 2 = 4 x^2+4y^2=4 x 2 + 4 y 2 = 4 z = 3 − x z=3−x z = 3 − x z = x − 3 z=x−3 z = x − 3
∫ − 1 1 ∫ − 4 − 4 y 2 4 − 4 y 2 ∫ x − 3 3 − x d z d x d y = 12 π \displaystyle\int_{-1}^1 \displaystyle\int_{-\sqrt{4-4y^2}}^{\sqrt{4-4y^2}} \displaystyle\int_{x-3}^{3-x} \ dz\ dx\ dy = 12\pi ∫ − 1 1 ∫ − 4 − 4 y 2 4 − 4 y 2 ∫ x − 3 3 − x d z d x d y = 1 2 π
Rewrite the integral ∫ 0 5 ∫ − 1 0 ∫ 0 4 x + 4 d y d x d z \displaystyle\int_0^5 \displaystyle\int_{-1}^0 \displaystyle\int_0^{4x+4}\ dy\ dx\ dz ∫ 0 5 ∫ − 1 0 ∫ 0 4 x + 4 d y d x d z d z d x d y dz\ dx\ dy d z d x d y
∫ 0 4 ∫ y / 4 − 1 0 ∫ 0 5 d z d x d y = 10 \displaystyle\int_0^4 \displaystyle\int_{y/4-1}^0 \displaystyle\int_0^5 \ dz\ dx\ dy = 10 ∫ 0 4 ∫ y / 4 − 1 0 ∫ 0 5 d z d x d y = 1 0
Evaluate the integral ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 − x 2 ∫ 0 1 − x 2 d z d y d x . \displaystyle\int_0^1 \displaystyle\int_0^{\sqrt{1-x^2}} \displaystyle\int_0^{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\ dz\ dy\ dx. ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 − x 2 ∫ 0 1 − x 2 d z d y d x .
2 3 \dfrac{2}{3} 3 2
Evaluate the integral ∫ 1 6 ∫ 0 4 − 2 y / 3 ∫ 0 12 − 2 y − 3 z 1 y d x d z d y . \displaystyle\int_1^6 \displaystyle\int_0^{4-2y/3} \displaystyle\int_0^{12-2y-3z} \dfrac{1}{y}\ dx\ dz\ dy. ∫ 1 6 ∫ 0 4 − 2 y / 3 ∫ 0 1 2 − 2 y − 3 z y 1 d x d z d y .
− 45 + 24 ln 6 -45+24\ln 6 − 4 5 + 2 4 ln 6